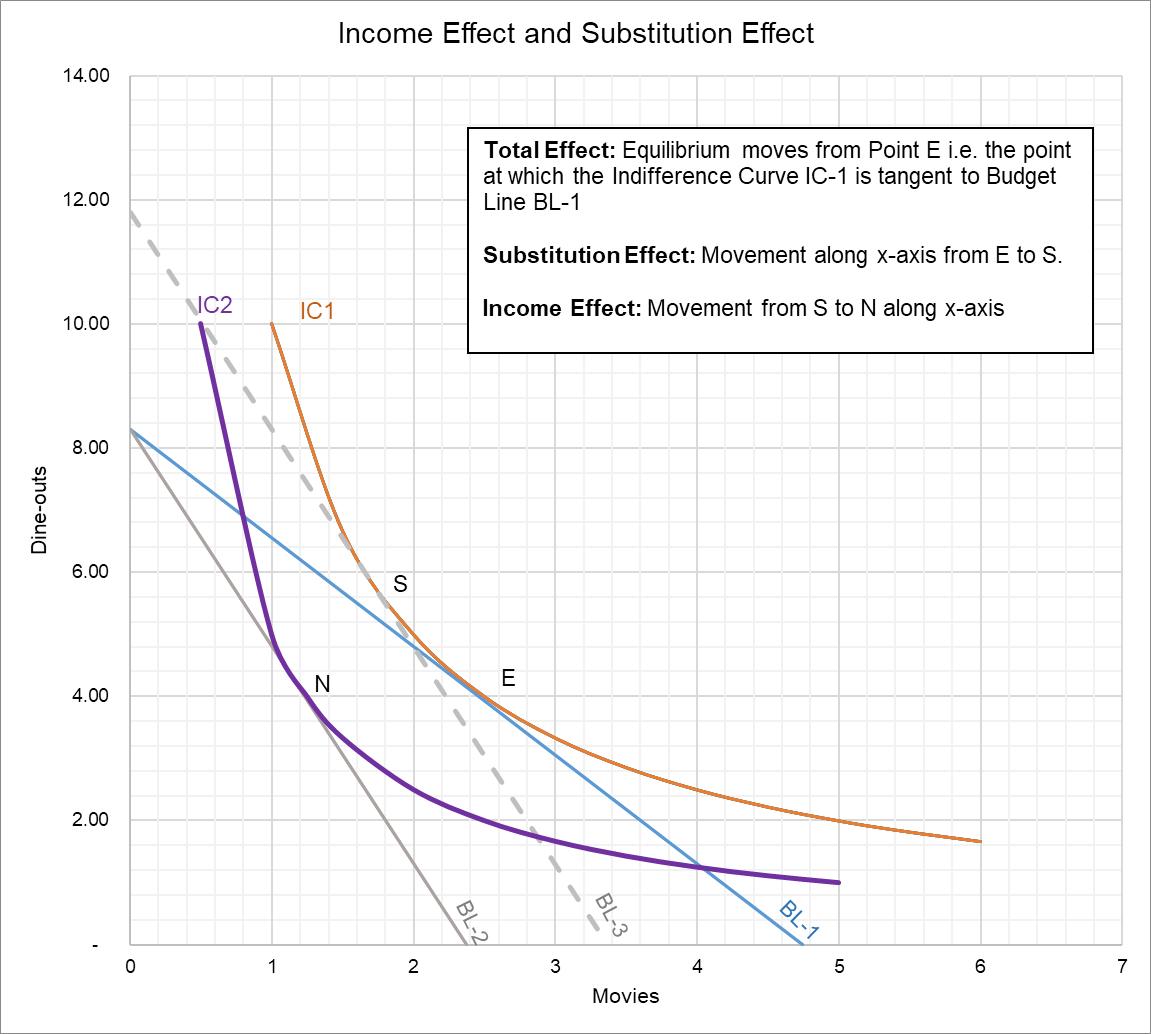
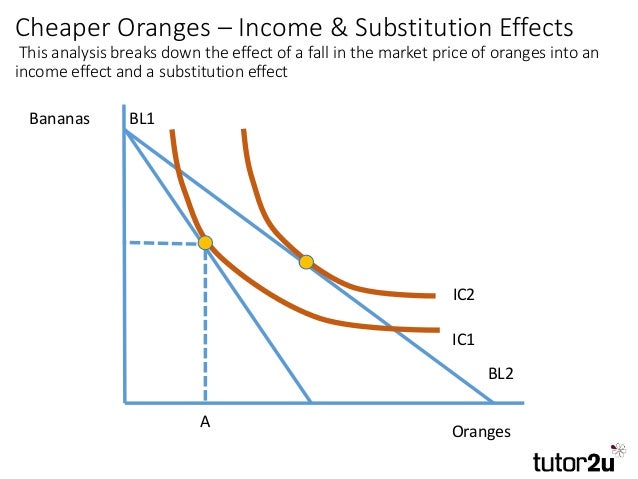
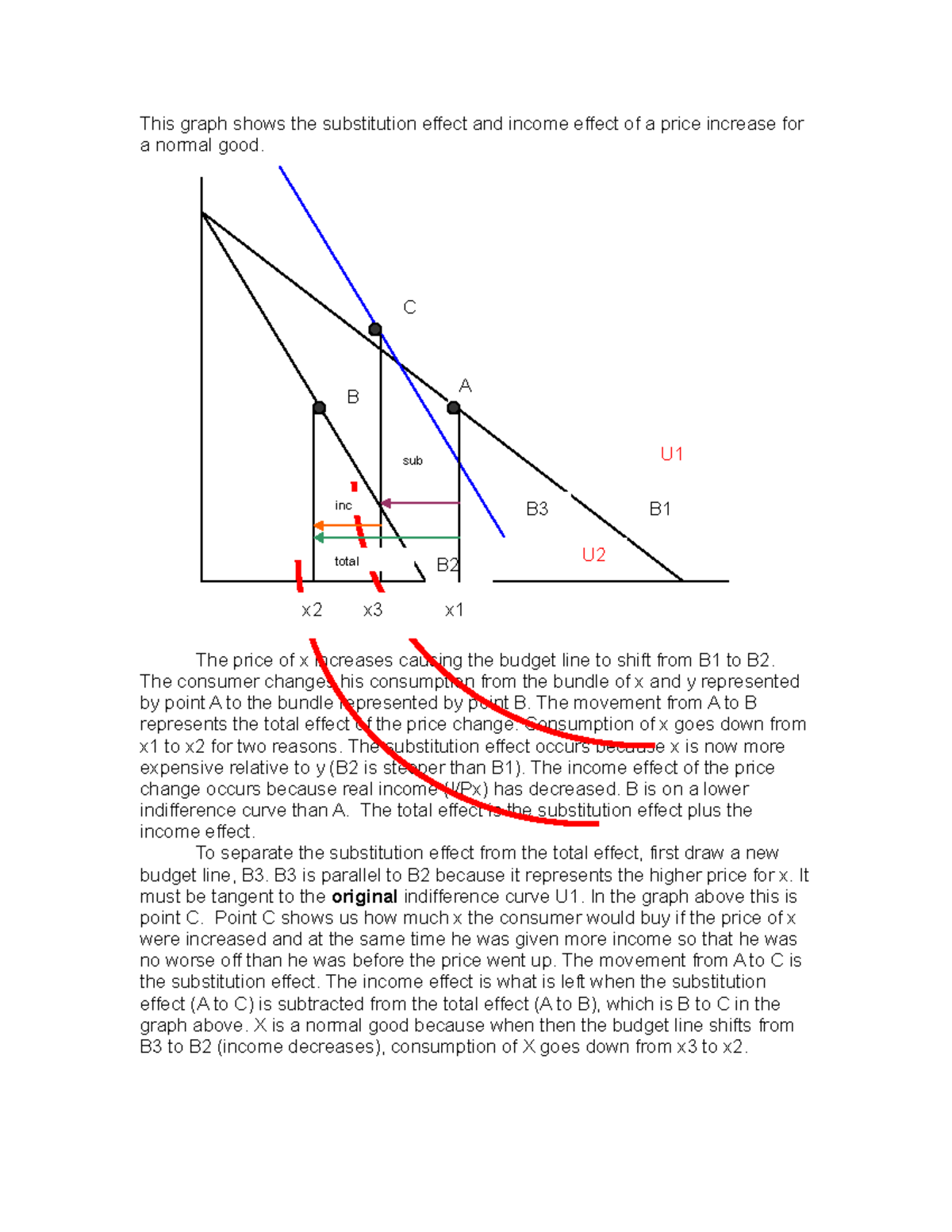
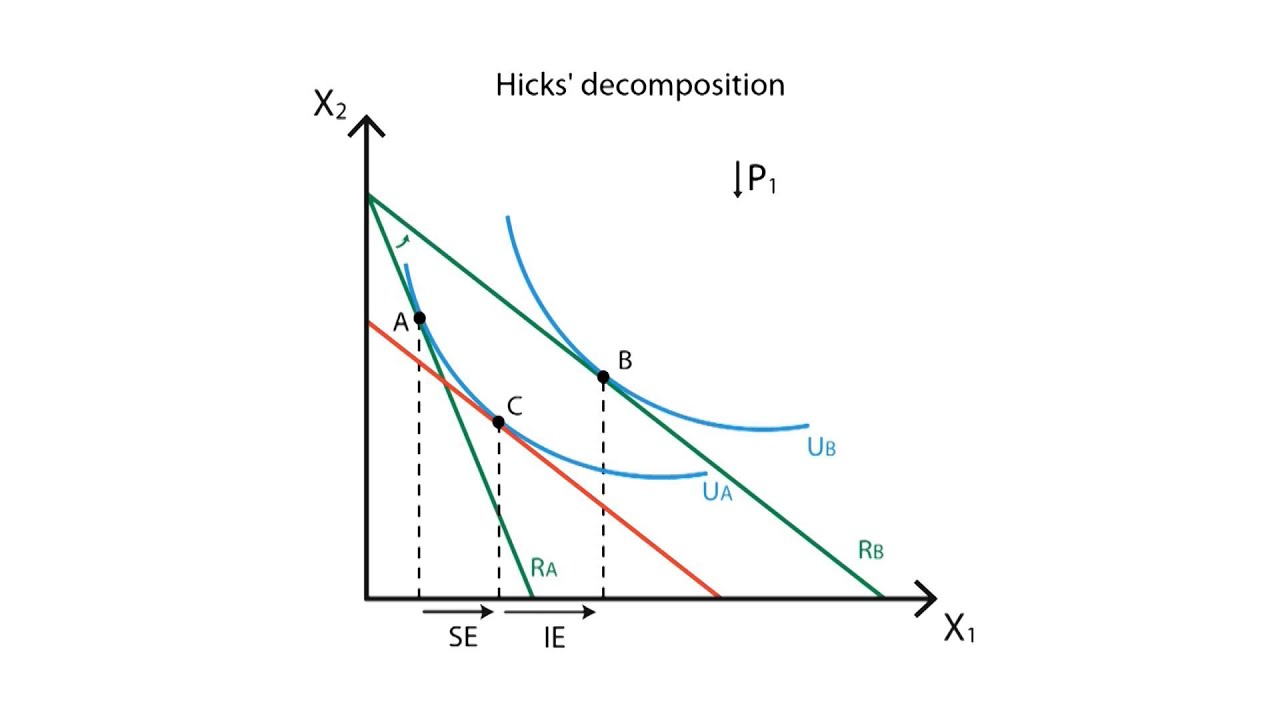
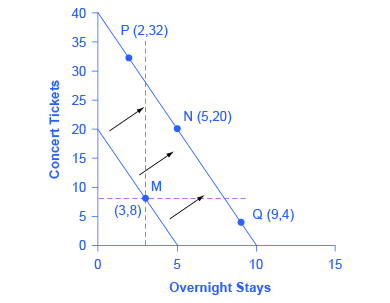
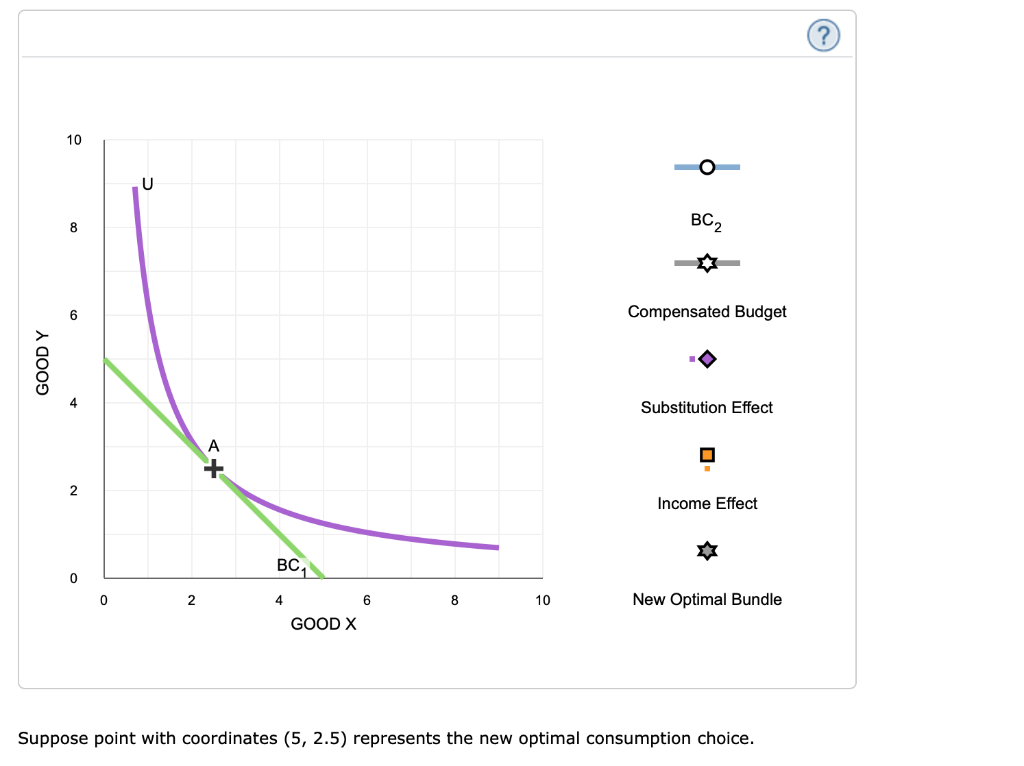
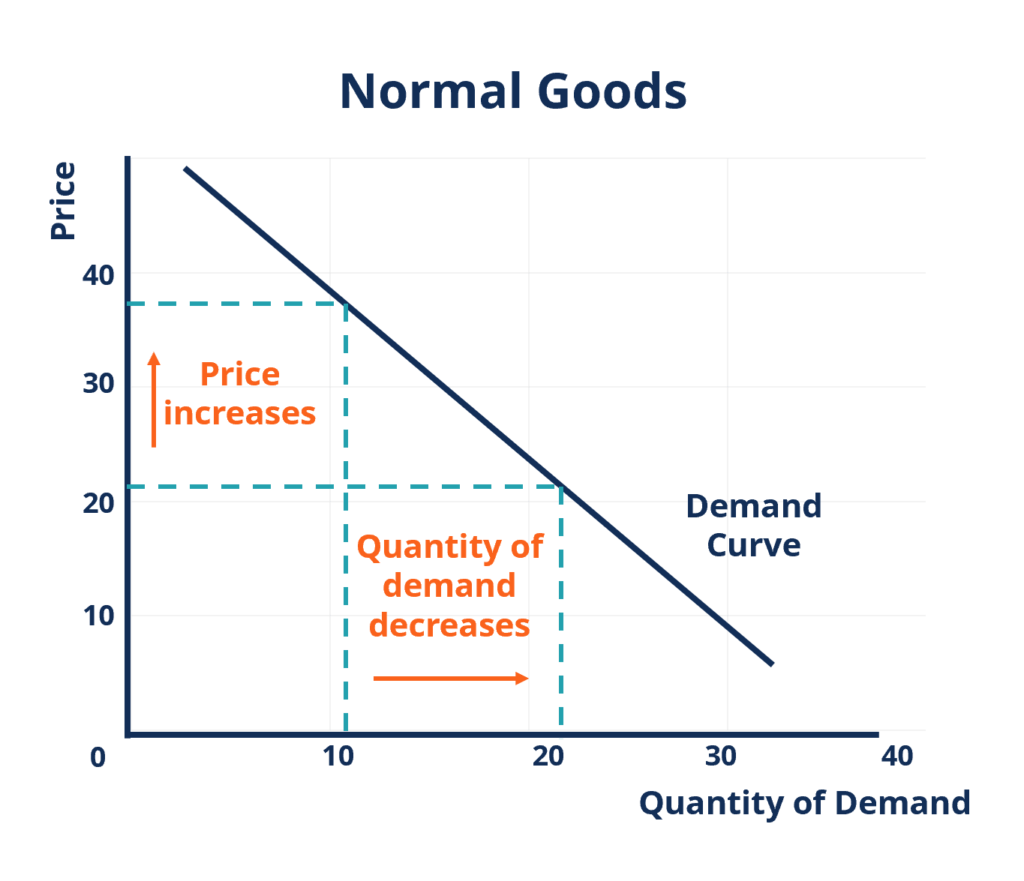
Income And Substitution Effect Graph For Normal Good

However if x were an inferior good then the income effect would be negative.
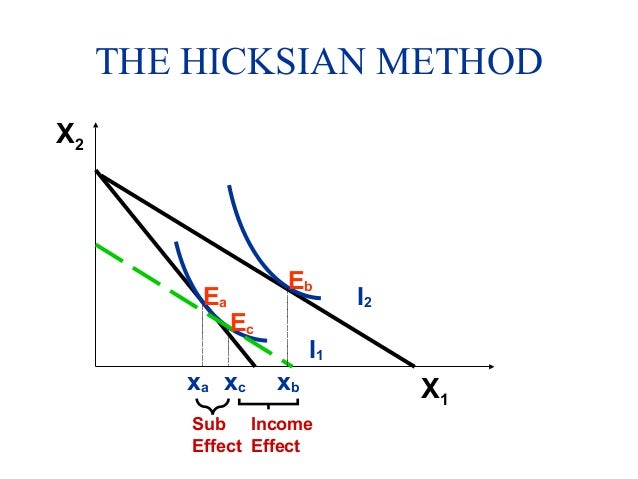
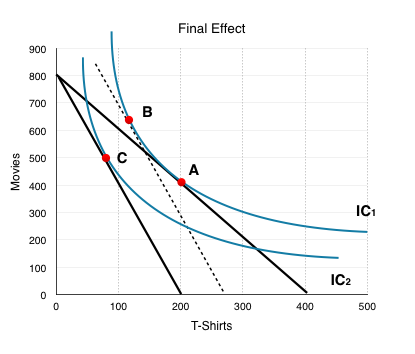
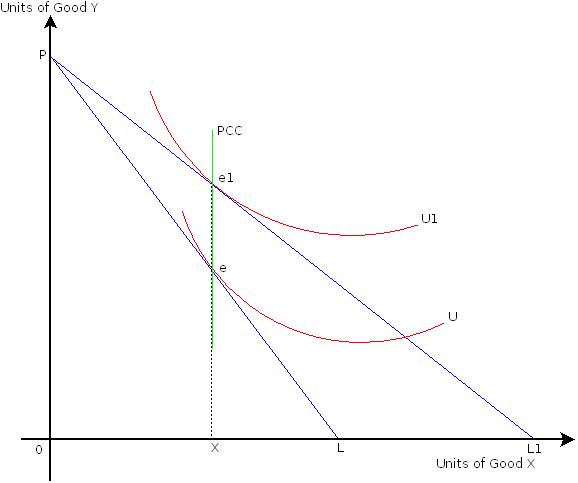
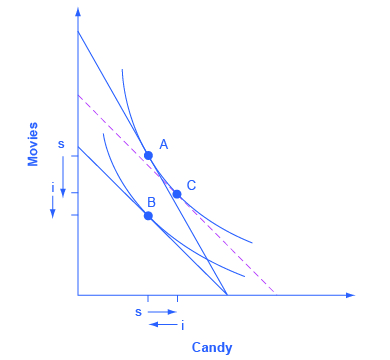
Income and substitution effect graph for normal good. X is a normal good because when then the budget line shifts from b3 to b2 income decreases consumption of x goes down from x3 to x2. The income effect is what is left when the substitution effect a to c is subtracted from the total effect a to b which is b to c in the graph above. The example discussed above is a normal good and hence the substitution effect and income effect work in tandem. They work in the same direction.
Income and substitution effects on giffen goods. In figure 1 the consumer s initial equilibrium point is e 1 where original budget line m 1 n 1 is tangent to the indifference curve ic 1 x axis represent giffen goods commodity x and y axis denotes superior goods commodity y. Normal good increase in price of good x a b c e 1 e 2 e starting point ending point imaginary point substitution effect 7 starting point imaginary point income effect 3 imaginary point ending point total effect 10 starting point ending point. In this case both the substitution and the income effects increase the quantity of x consumed.