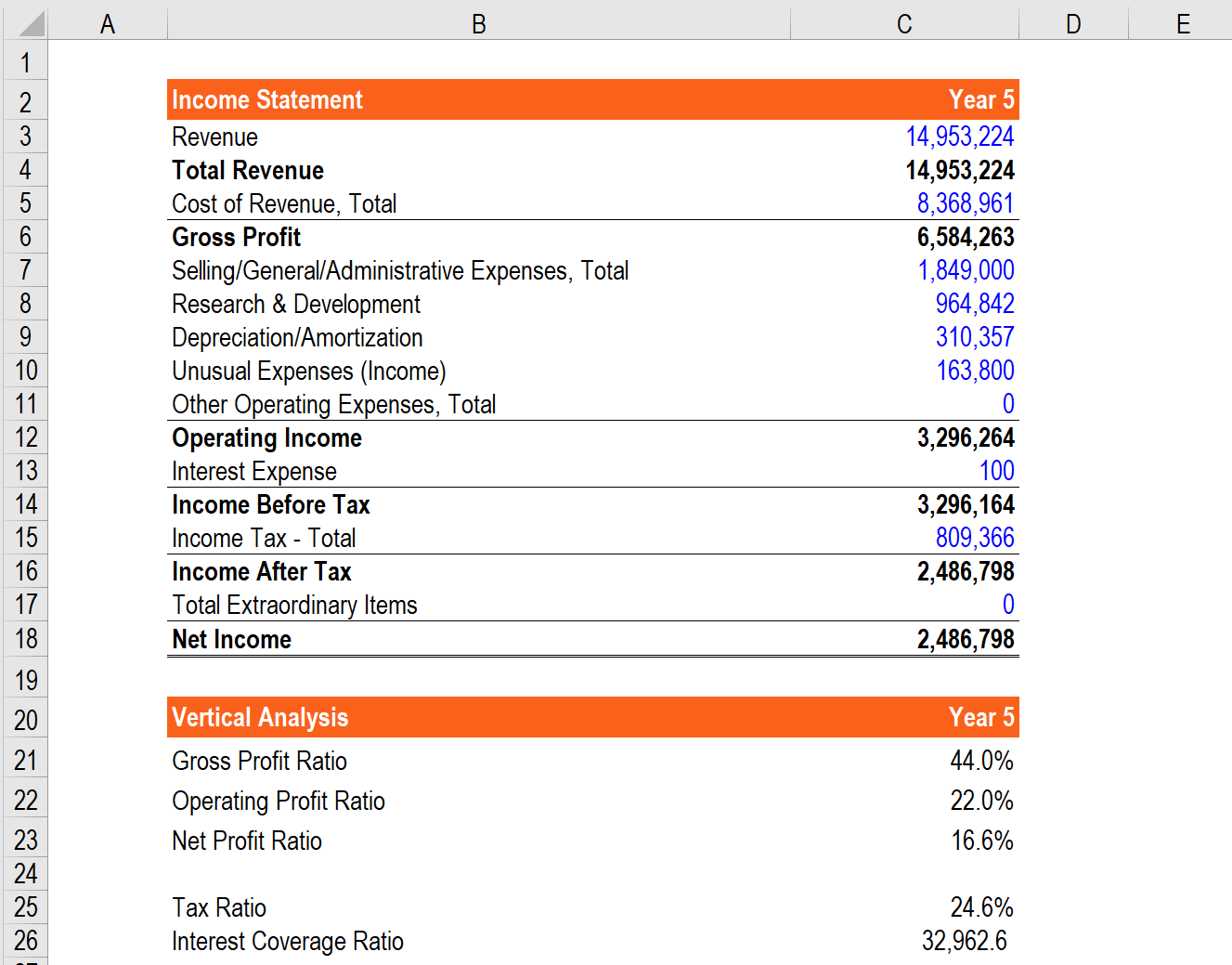
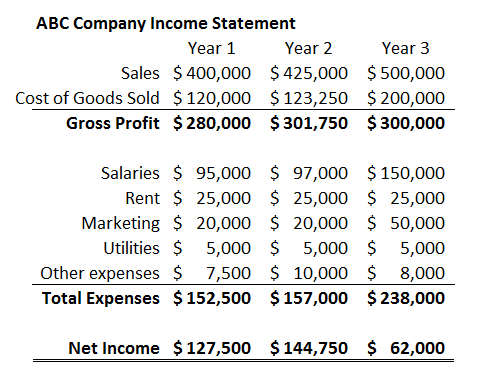
Income Statement Horizontal Analysis Definition

Horizontal analysis also known as trend analysis is a financial statement analysis technique that shows changes in the amounts of corresponding financial statement items over a period of time.
Income statement horizontal analysis definition. For instance instead of creating a balance sheet or income statement for one specific period of. It is usually depicted as a percentage growth over the same line item in the base year. Horizontal analysis is a procedure in the fundamental analysis in which the amounts of financial information over a certain period of time is compared line by line in order to make related decisions. Horizontal analysis of financial statements is one of the most important techniques to find out how a company is doing financially.
The case for both the question isn t whether you should be leveraging vertical or horizontal analysis when evaluating income statements. It is used for evaluating trends year over year yoy or quarter over quarter qoq. Horizontal analysis is used in the review of a company s financial statements over multiple periods. Horizontal analysis calculates the amount and percentage changes in financial figures from one period to another period of time.
In other words it compares financial data for at least two years months quarters periods. The objective is to find out the change in financial figures as well as the direction of such change. Vertical analysis is the method of analysis of financial statements where each line item is listed as a percentage of another item to assist decision making. What is horizontal analysis.
The statements for two or more periods are used in horizontal analysis. The earliest year presented is designated as the base year and the subsequent years are expressed as a percentage of the base year amounts. Horizontal or trend analysis is used to spot and evaluate trends over a specific period of time. Ultimately horizontal analysis is used to identify trends over time comparisons from q1 to q2 for example instead of revealing how individual line items relate to others.
It is used to see if any numbers are unusually high or low in comparison to the information for bracketing periods which may then trigger a detailed investigation of the reason for the difference. This method involves financial statements reporting amounts for several years.





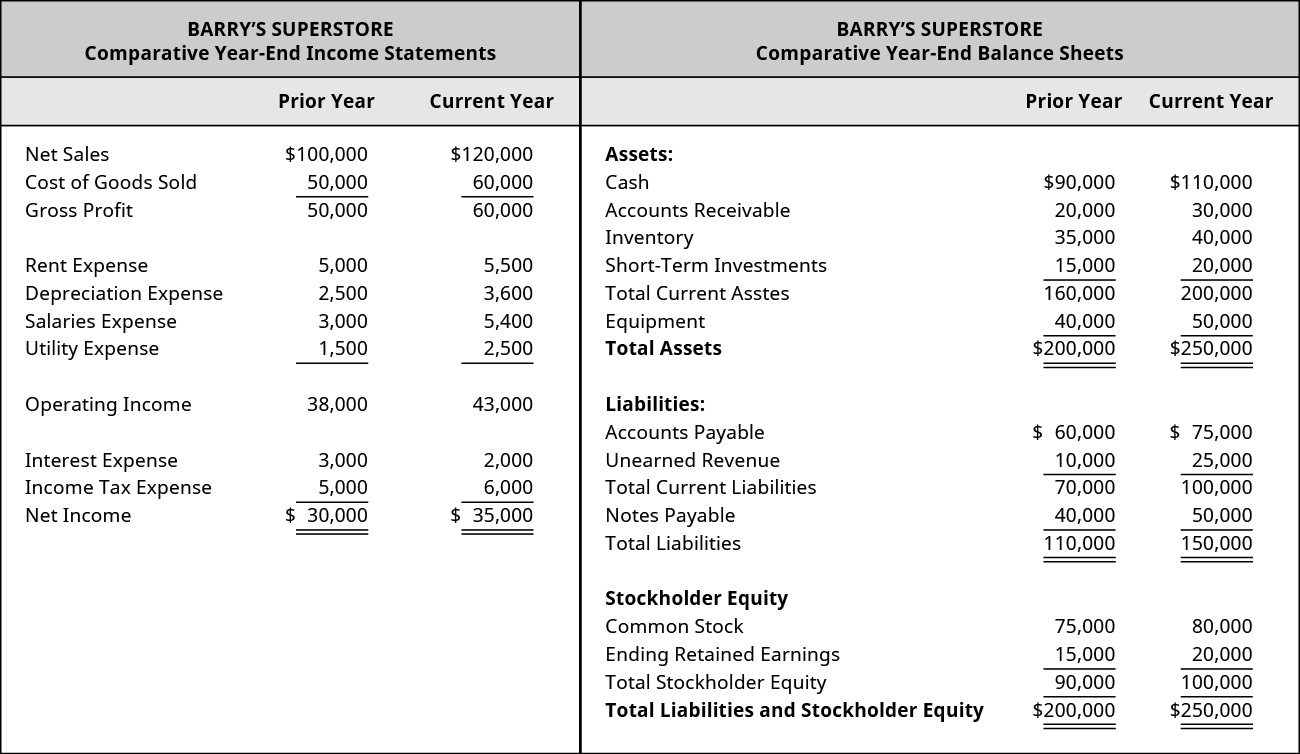
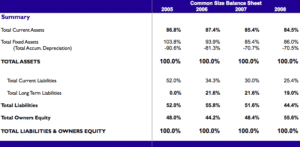

/dotdash_Final_Common_Size_Income_Statement_Oct_2020-01-f6706faee5644055954e9e5675485a5e.jpg)