Income Tax Definition Ww1
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-182885962-980f463243df44ba9f5495b7f5fb15c5.jpg)
The act was sponsored by representative oscar underwood passed by the 63rd united states congress and signed into law by president woodrow wilson.
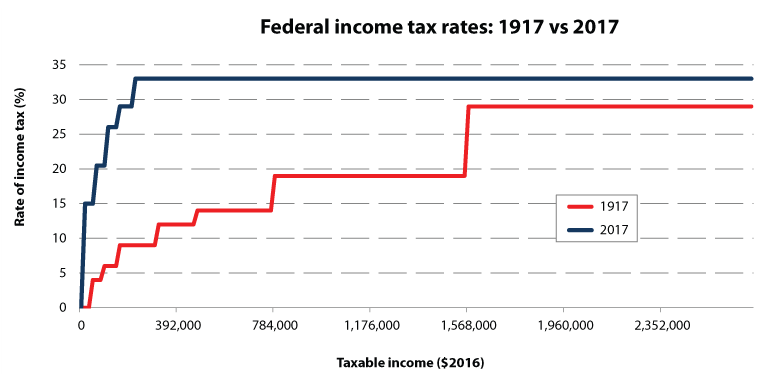
Income tax definition ww1. War finance is a branch of defense economics. 114 re established a federal income tax in the united states and substantially lowered tariff rates. Under the 1917 act a taxpayer with an income of only 40 000 was subject to a 16 percent tax rate while one who earned 1 5 million faced a rate of 67 percent. The revenue act of 1913 also known as the underwood tariff or the underwood simmons act ch.
That amount was lowered to 2 000. The income tax was introduced because other forms of taxation were becoming unfeasible. Corporate income taxes actually restrict corporate growth to some extent. The top bracket on income above 2 million was raised from 15 to 67.
Easton burns a certified accountant goes through the act clause by clause to discuss its full impact on canadians. Ww1 didn t start until 1914 and the u s. The highest income tax rate jumped from 15 percent in 1916 to 67 percent in 1917 to 77 percent in 1918. The 2 bracket had previously applied to income below 20 000.
The war revenue act of 1917 including the war income tax and the war excess profits tax and the federal income tax law of 1916 as amended 1917. The income tax is charged or levied as a pe tax rates flat tax provision issue a flat tax taxes everybody at the same tax rate. Didn t join the war until 1917. The united states war revenue act of 1917 greatly increased federal income tax rates while simultaneously lowering exemptions.
A graduated tax taxes at different tax rates. Income tax 1917 originally presented as a temporary wartime measure the income war tax act of 1917 was viewed as a controversial measure at the time. Income tax an income tax is a portion of an individual or business s earnings that is collected by the government. Of the three only britain eventually adopted an income tax before the coming of war.
The government spending was exceeding the amounts that could be collected from excise taxes and tariffs. It has been argued that in germany the financial constraints imposed by the necessity of raising funds through the federal states that made up the empire shackled military expenditures before 1914 to the detriment of german power. The 2 bracket had previously applied to income below 20 000. After the war federal income tax rates took on the steam of the roaring 1920s dropping to 25 percent from 1925 through 1931.
Major wars are usually financed to some extent by inflationary measures. In the late 1990s flat tax united states. War finance fiscal and monetary methods used in meeting the costs of war including taxation compulsory loans voluntary domestic loans foreign loans and the creation of money.