Does Income Statement Include Accounts Receivable
The balance in the accounts receivable account is comprised of all unpaid receivables.
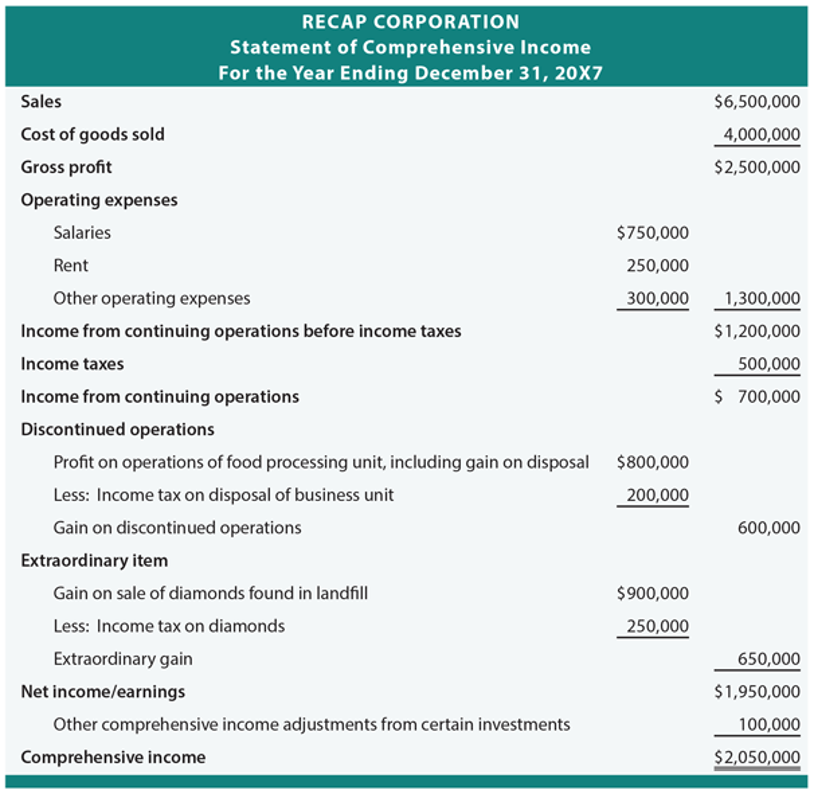
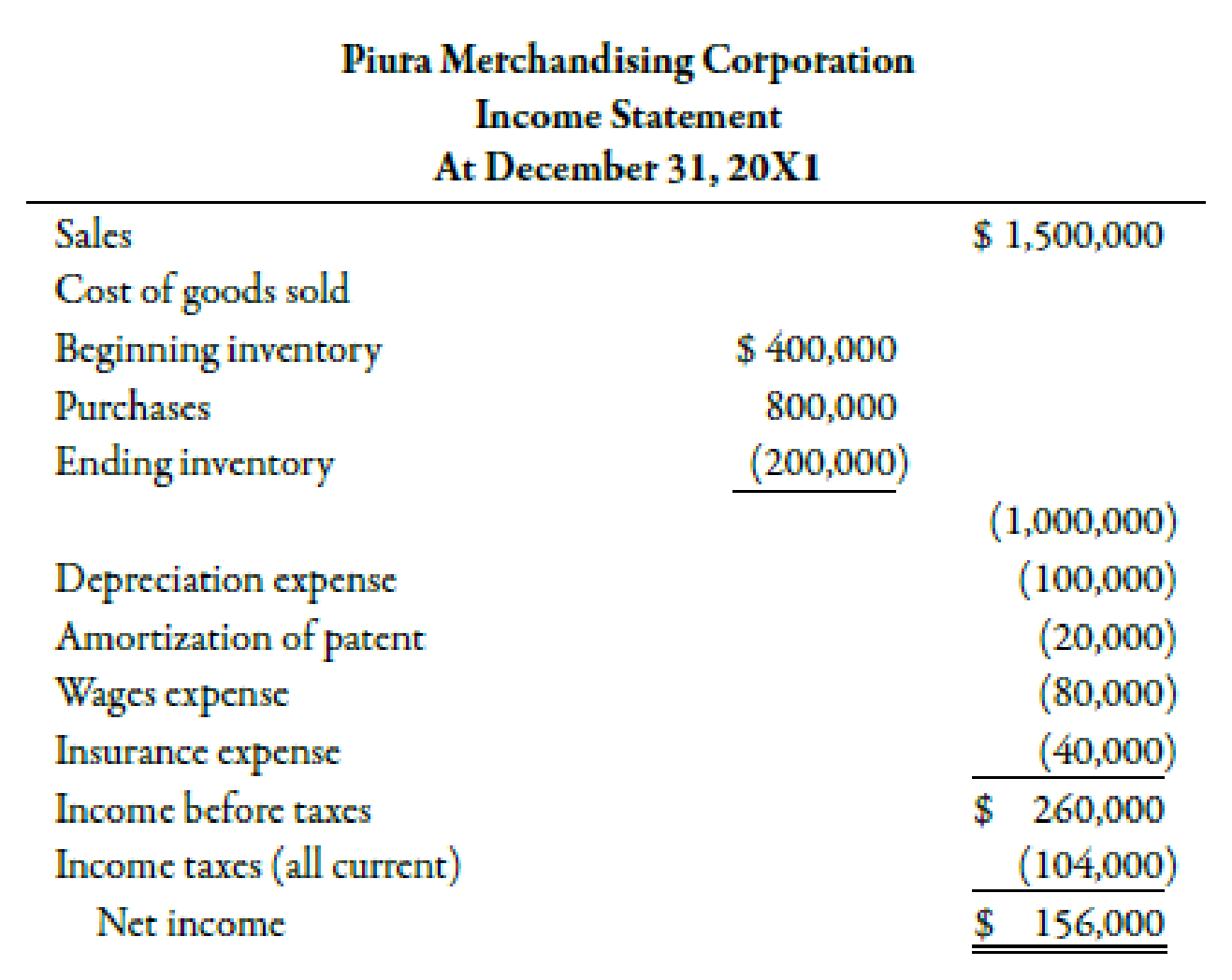
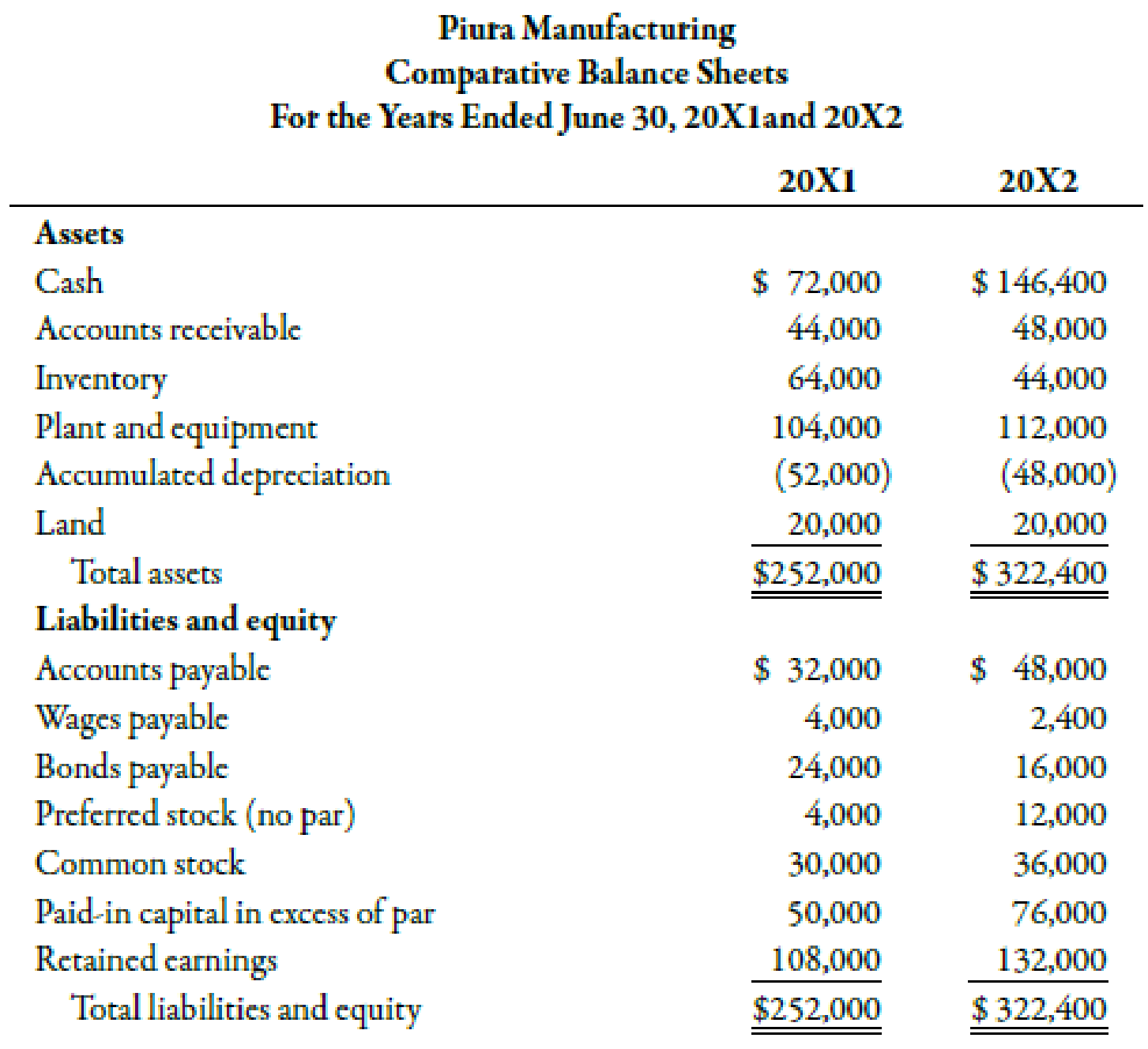
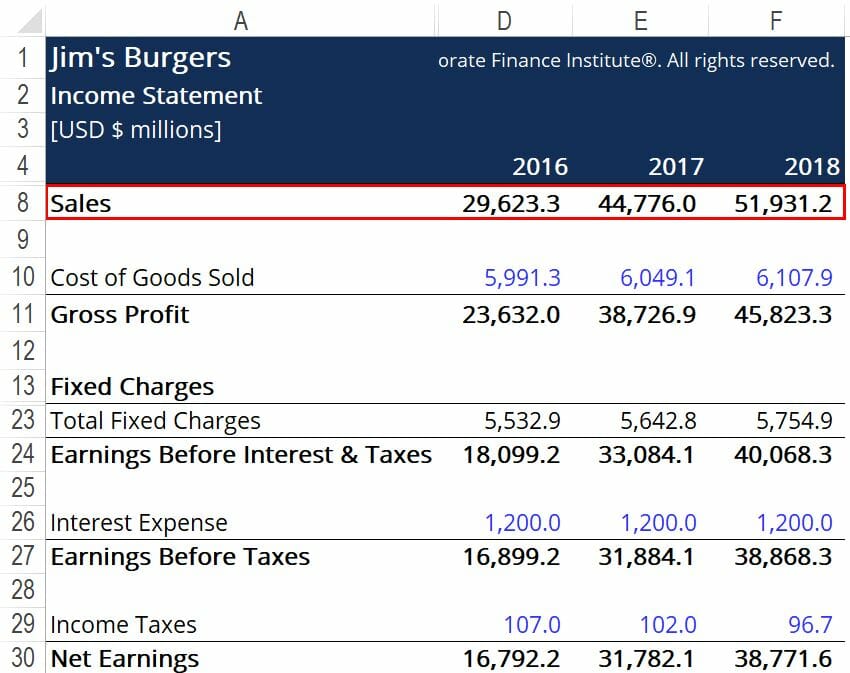
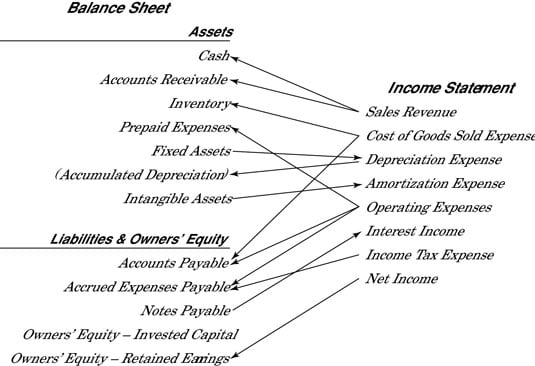
Does income statement include accounts receivable. This amount appears in the top line of the income statement. The gross amount recorded for the sales of goods and services is revenue. Accounts receivables would be included in the balance sheet. This typically means that the account balance includes unpaid invoice balances from both the current and prior periods.
This means that typically the account balance includes unpaid invoice balances from both prior and current periods. It is popularly called trade receivables and it is a current asset. So technically yes the account receivable account is in the balance sheet its the offsetting revenue that is in the income statement. The corresponding amount equivalent to accounts receivables are recorded as sales.
The amount due from the customer is called accounts receivables. No ar is an asset on the balance sheet. Accounts receivable also known as customer receivables don t go on an income statement which is what finance people often call a statement of profit and loss or p l. The income statement reports revenues and expenses.
Revenue is on the income statement. Accounts receivables is an asset account and all the asset liablities and equity. An account receivable is included in the income statement no different than a cash sale as sales or revenue. Money that customers owe a company flows through the statement of financial position also referred to as a balance sheet or report on financial condition.
In the accounts receivable account the balance is comprised of all unpaid receivables. This amount is shown on the top line of the income statement. Generally speaking net income is revenues minus expenses under the accrual basis of accounting revenues and accounts receivable are recorded when a company sells products or earns fees by providing services on credit. Accounts receivable represents a.
Revenue is the gross amount recorded for the sale of goods or services. The only difference is that the seller has allowed the buyer additional time to pay for the purchase.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-01-3998c75d45bb4811ad235ef4eaf17593.jpg)
/dotdash_Final_What_Changes_in_Working_Capital_Impact_Cash_Flow_Sep_2020-01-13de858aa25b4c5389427b3f49bef9bc.jpg)
/dotdash_Final_Understanding_the_Cash_Flow_Statement_Jul_2020-01-013298d8e8ac425cb2ccd753e04bf8b6.jpg)
