Income And Substitution Effect Labor Supply
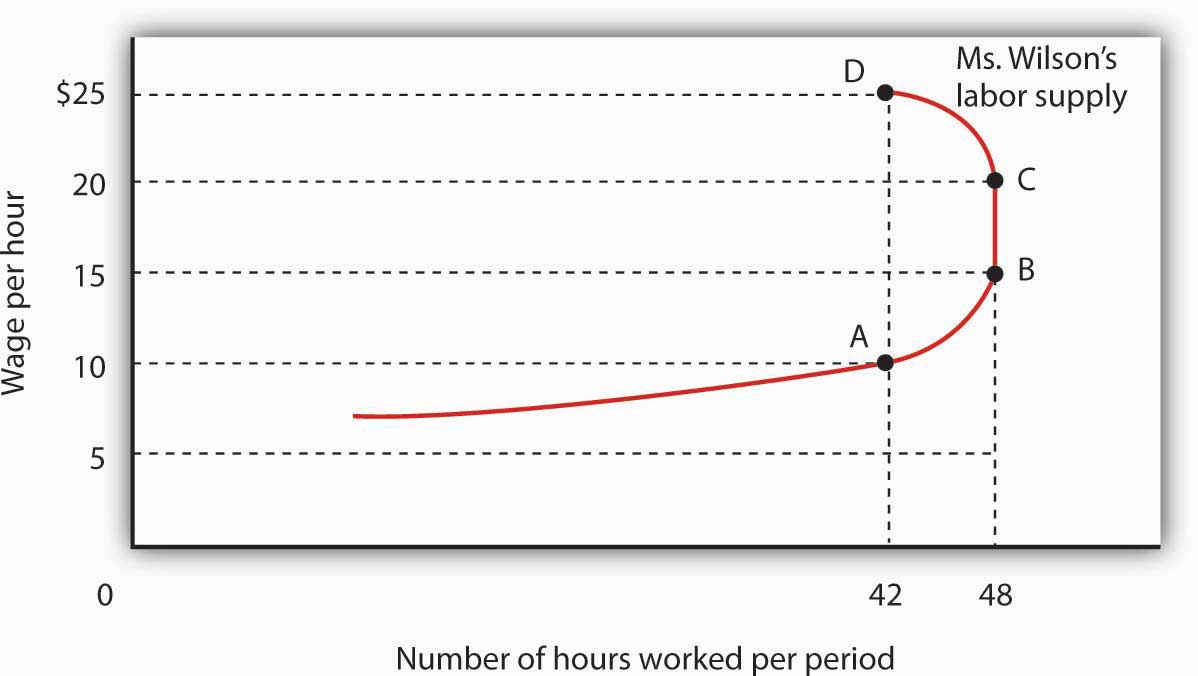
The substitution and income effects influence meredith wilson s supply of labor when she gets a pay raise.
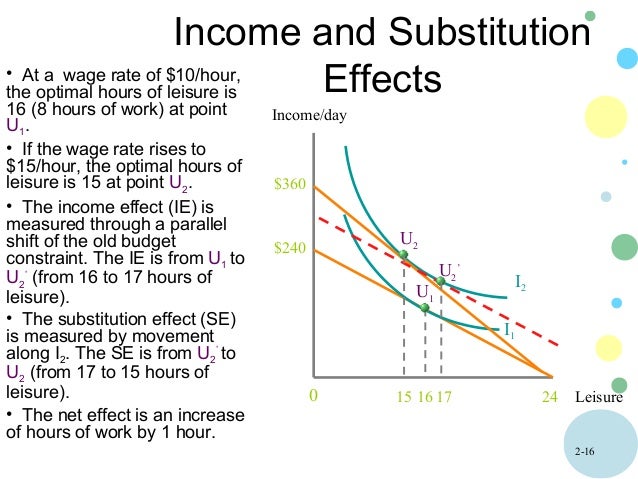
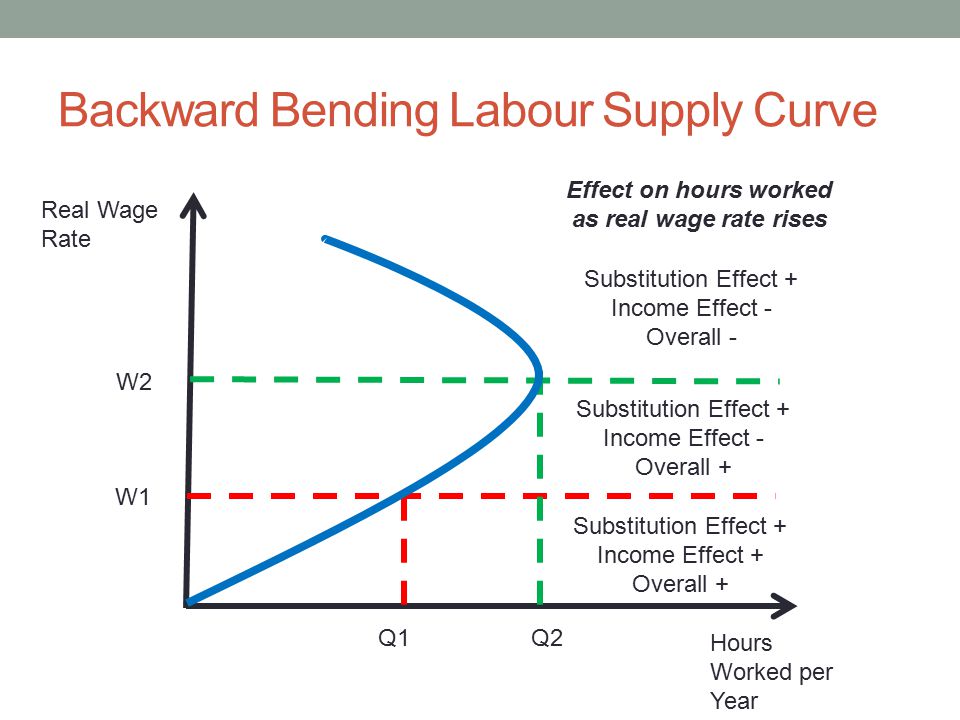
Income and substitution effect labor supply. The income effect of a rise in the hourly wage rate. At a wage of 10 per hour she supplies 42 hours of work per week point a. Let s keep using the coffee shop example. If leisure is an inferior good both substitution effect and income effect work in the same.
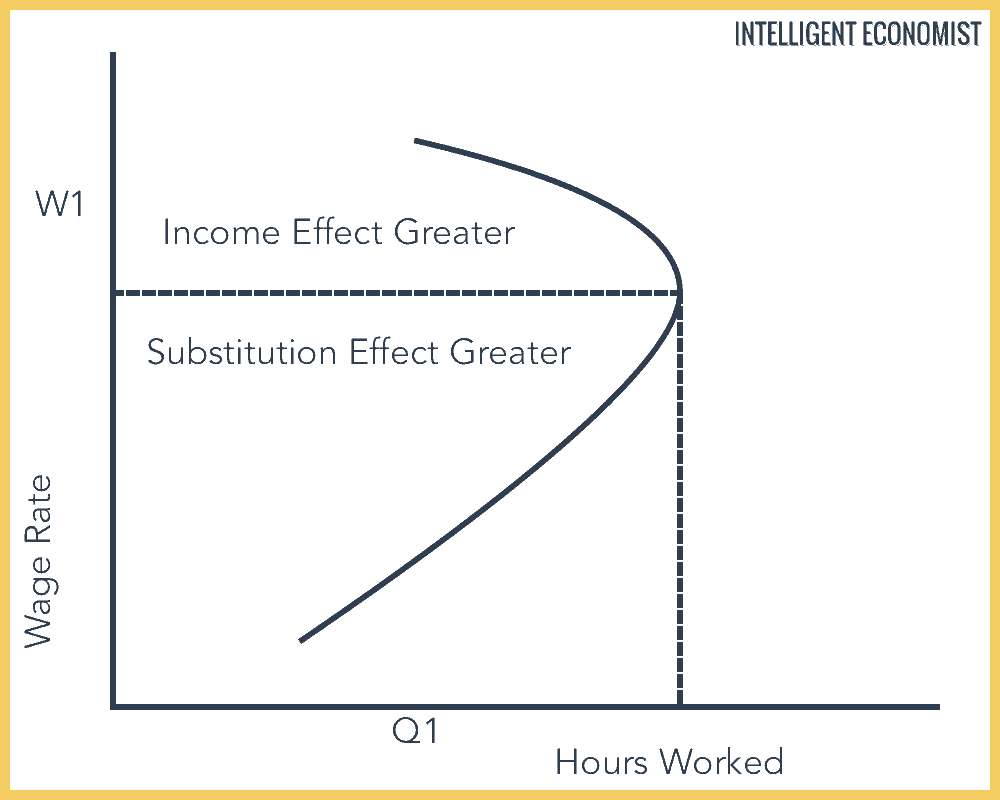
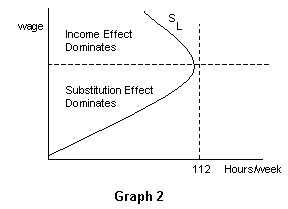
Labor supply is unresponsive to permanent changes in wage rates. This effect is relevant to the individual labour supply curve rather the industry labour supply curve. At 15 per hour the substitution effect pulls in the direction of an increased quantity of labor supplied and the income effect pulls in the opposite direction. The income effect expresses the impact of higher purchasing power on consumption.
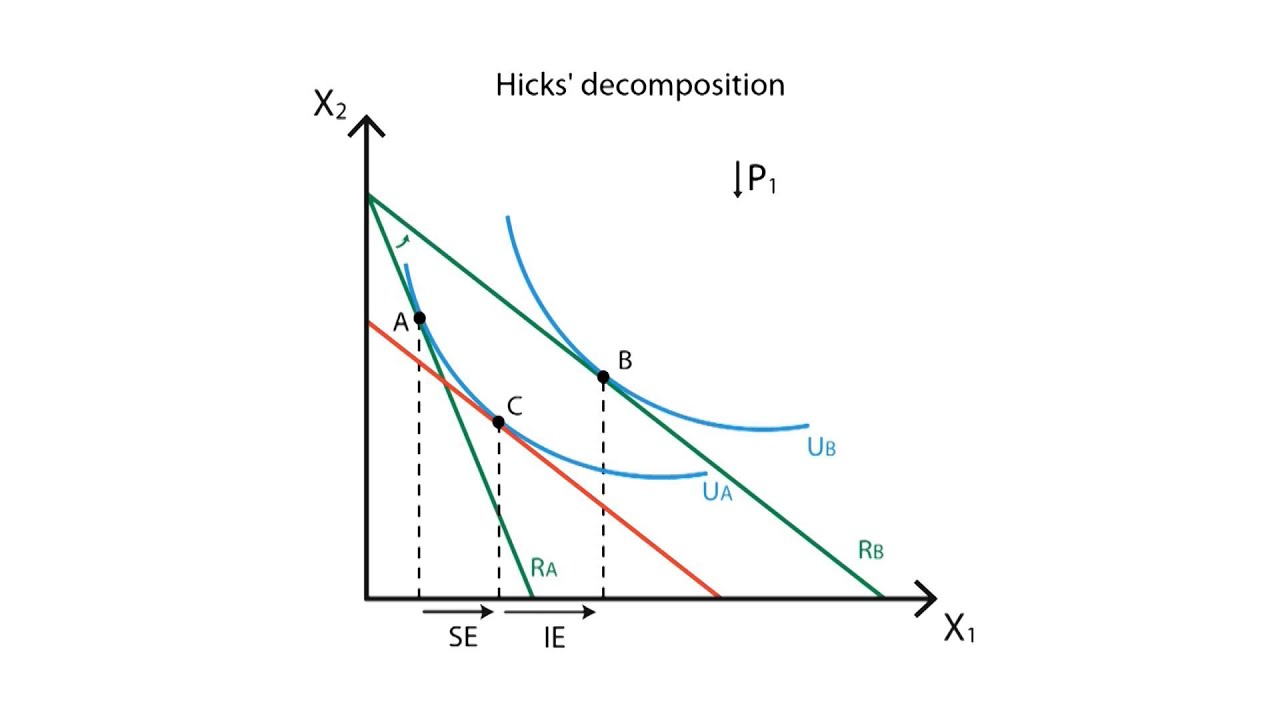
When higher wages cause people to want to work more hours in order to reach a target desired income. So his labour supply curve bends back to the left. The substitution effect describes how consumption is impacted by changing relative income and prices. The substitution effect.
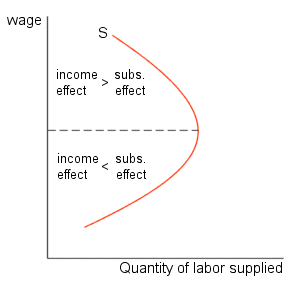
Many studies have demonstrated that the price elasticity of labor supply is positive meaning that the substitution effect dominates more than the income effect in aggregate. This is essential to a fundamental knowledge of labor market economics as we understand it today. This paper develops a theory of labor supply where income and substitution effects cancel taking into account optimization over time fixed costs of going to work and interactions of. A s income effect outweighs the substitution effect the total effect of wage rise on leisure is positive n 2 n 1 and h 2 h 1.
Both the income effect and the substitution effect can have massive impacts on supply and demand. A works fewer hours as the wage rate rises. When a target income has been reached and people prefer spending more time on leisure rather than earning more income.