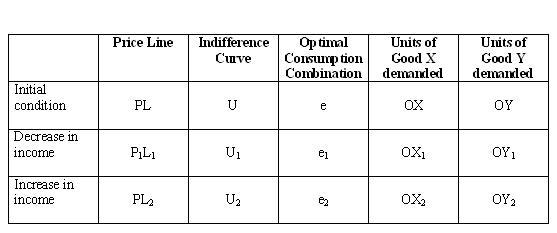
Income And Substitution Effect Table
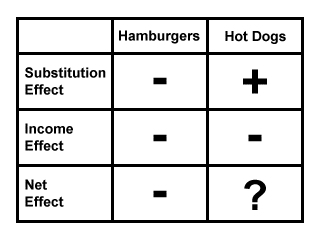
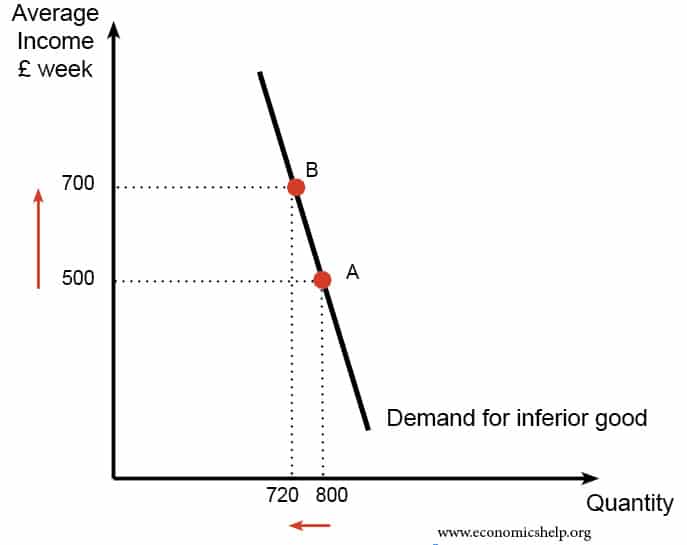
Income and substitution effects on inferior goods.
Income and substitution effect table. Sections 14 1 17 1 and 17 3 of malcolm pemberton and nicholas rau. Real income of the consumer. Income effect b the income effect is the movement from point c to point b if x1 is a normal good the individual will buy more because real income increased 18 income effect the income effect caused by a change in price from p1 to p1 is the difference between the total change and the substitution effect. People use inferior goods when they are unable to afford normal goods or expensive goods.
Income and substitution effects for goods. Income effect and substitution effect are the components of price effect i e. Second there is an income effect whereby the fall in the price of good 1 changes leads to an increase in the purchasing power i e. Therefore consumption of inferior goods by a person decreases if income increases above a.
Income and substitution effects yp m 1 xp m 2 xp m y x price of y and monetary income are held constant. Substitution effect x 1 x 2. The decrease in quantity demanded due to increase in price of a product. Substitution effect income effect total effect normal good price rises 0 0 0 price falls 0 0 0 inferior good price rises 0 0.
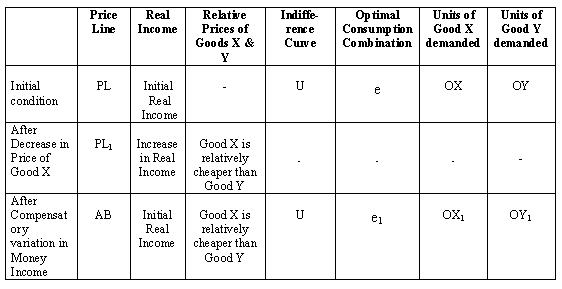
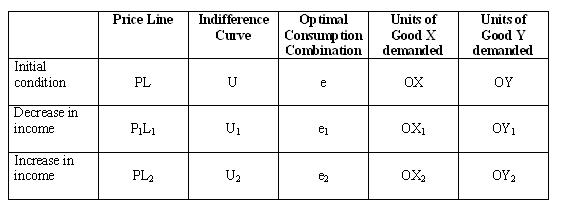
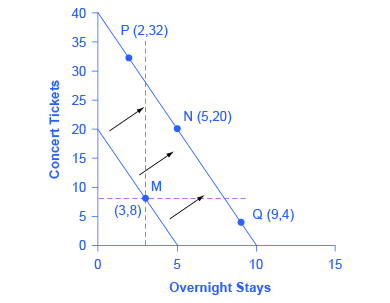
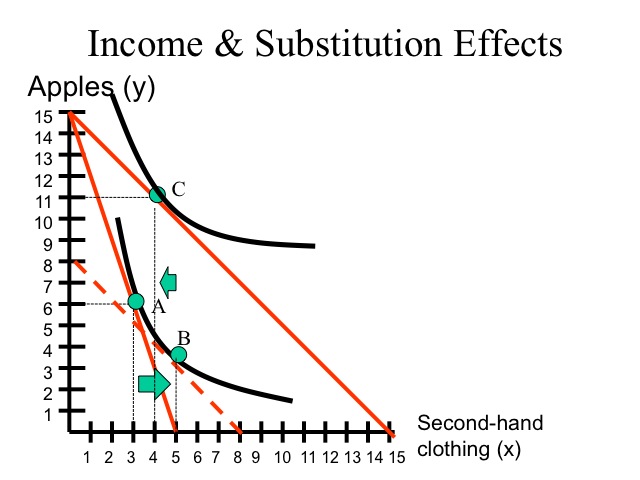
The decomposition of the price effect into the substitution and income effect components income and substitution effects of a price change can be done in several ways depending on what we would like to hold constant. Income effect arises because a price change changes a consumer s real income and substitution effect occurs when consumers opt for the product s substitutes. This is essential to a fundamental knowledge of labor market economics as we understand it today. In terms of figure 1 we measure the substitution effect from a b and the income effect from b c.
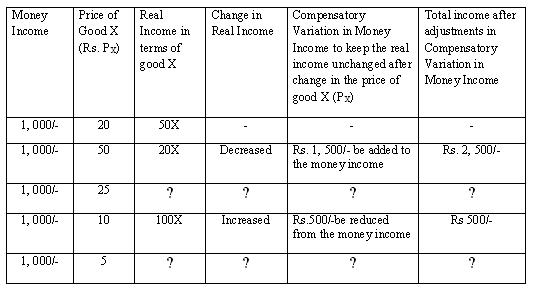
Mpy decrease in the price of x. The substitution effect is the effect on the choice of free time of changing the wage from 16 to 25 but also adjusting income to keep utility constant at 4 624. Aggregated income and substitution effects. The income effect expresses the impact of higher purchasing power on consumption.
Income effect x 2 x 3. Many studies have demonstrated that the price elasticity of labor supply is positive meaning that the substitution effect dominates more than the income effect in aggregate. The substitution effect describes how consumption is impacted by changing relative income and prices. 1 xp 2 xp 1x 2x 1y 2y 1u 2u e1 e2 yp px 1 yp px 2 te se total effect te substitution effect se income effect ie ie dr.