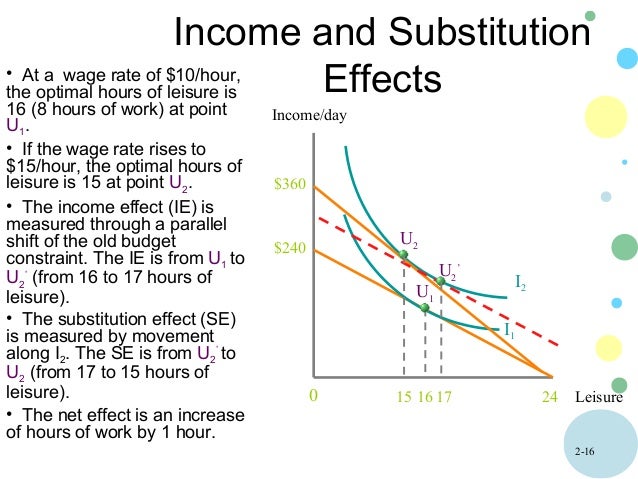
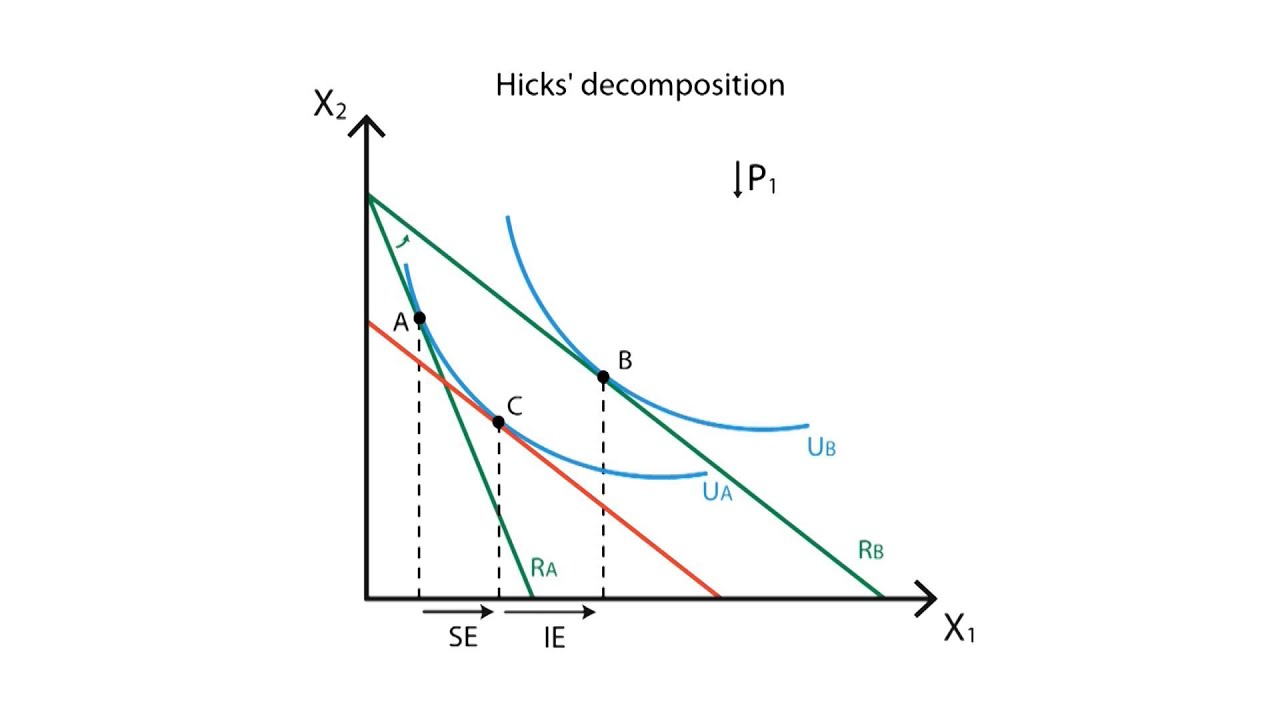
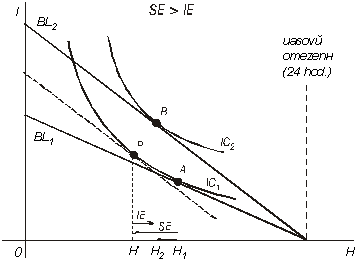
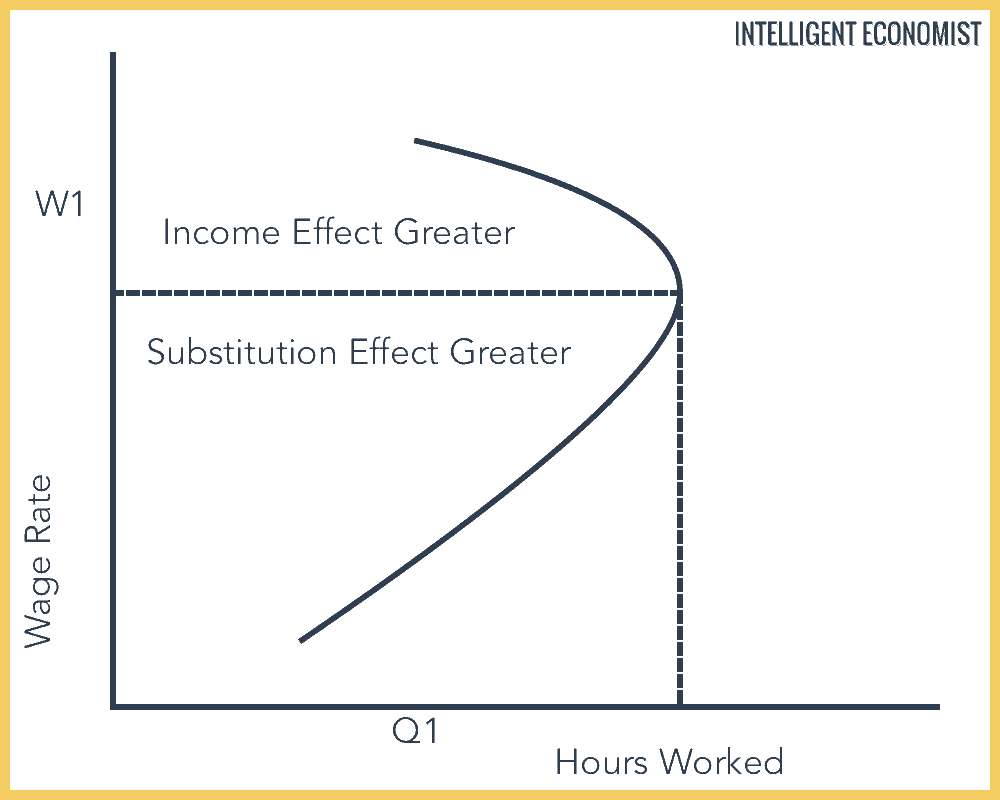
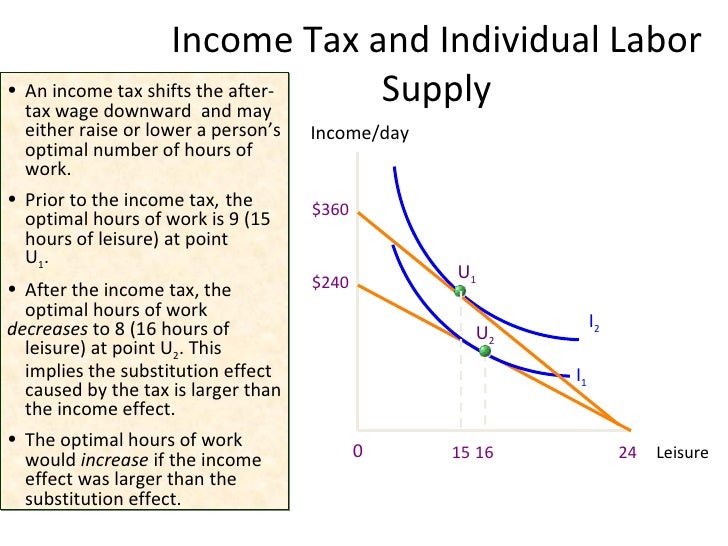
Income And Substitution Effect Work And Leisure

The opportunity cost of taking leisure is the monetary value of the wages foregone.
Income and substitution effect work and leisure. Income effect ie and substitution effect se. If the se is stronger than the ie individual will enjoy more leisure and consequently will work less as a result of the tax. It is thus clear that for an individual supplier of labour income effect and substitution effect work in opposite directions. The substitution effect of higher wages means workers will give up leisure to do more hours of work because work has now a higher reward.
The income effect of a rise in the hourly wage rate. When leisure is a normal good the substitution effect and the income effect work in opposite directions. Which of the two effects is the strongest. But the income effect is always negative.
The price of leisure however increases since you re higher paid each foregone hour is more expensive suggesting you will work more substitution effect. A higher wage implies a higher income and a higher income implies a greater demand for leisure and more leisure means a lower quantity of labor supplied. Does the substitution effect tell you to have more or less leisure time. Does the income effect or substitution effect dominate.
The net effect on individual work effort depends on the relative magnitudes of the two effects. This is a substitution effect of the rise in wage rate which tends to reduce leisure and increase labour supply i e. The income effect of higher wages means workers will reduce the amount of hours they work because they can maintain a target level of income through fewer hours. With the substitution and income effects working in opposite directions it is not clear whether a wage increase will increase or decrease the.
There is no universal standard to determine whether the income or substitution effect is more prevalent it all depends on. So whether leisure demand increases or not depends on which effect is stronger. A change in the wage rate has both an income effect and a substitution effect. Can you now afford more or less leisure time than at the old rate.
Number of hours worked. A s income effect outweighs the substitution effect the total effect of wage rise on leisure is positive n 2 n 1 and h 2 h 1. The substitution effect describes how consumption is impacted by changing relative income and prices. How about the income effect.