Income Effect Vs Substitution Effect Labor
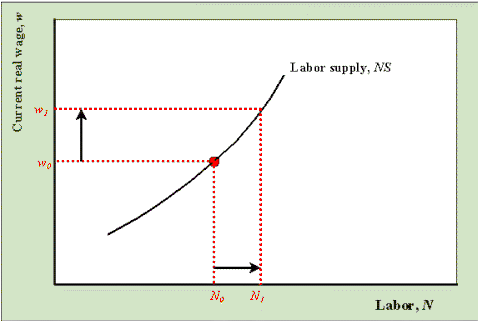
A change in the wage rate has both an income effect and a substitution effect.
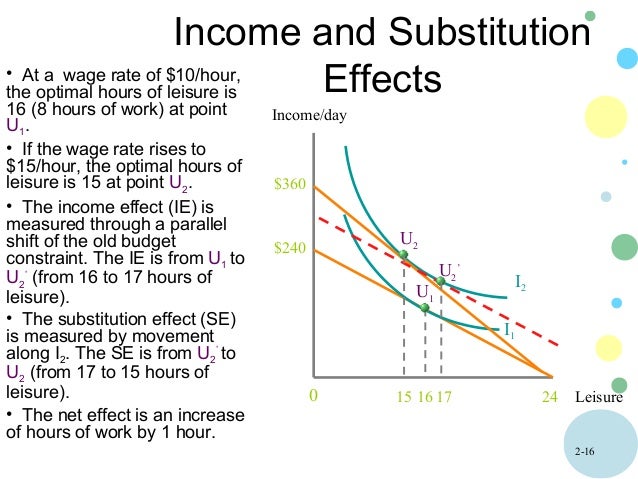
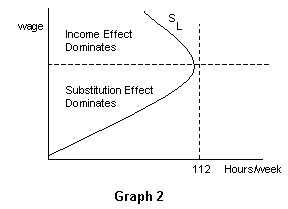
Income effect vs substitution effect labor. The effect of the wage increase on the quantity of labor ms. Thus income and substitution effects cancel but are they both close to zero or both large. Income effect substitution effect. A s income effect outweighs the substitution effect the total effect of wage rise on leisure is positive n 2 n 1 and h 2 h 1.
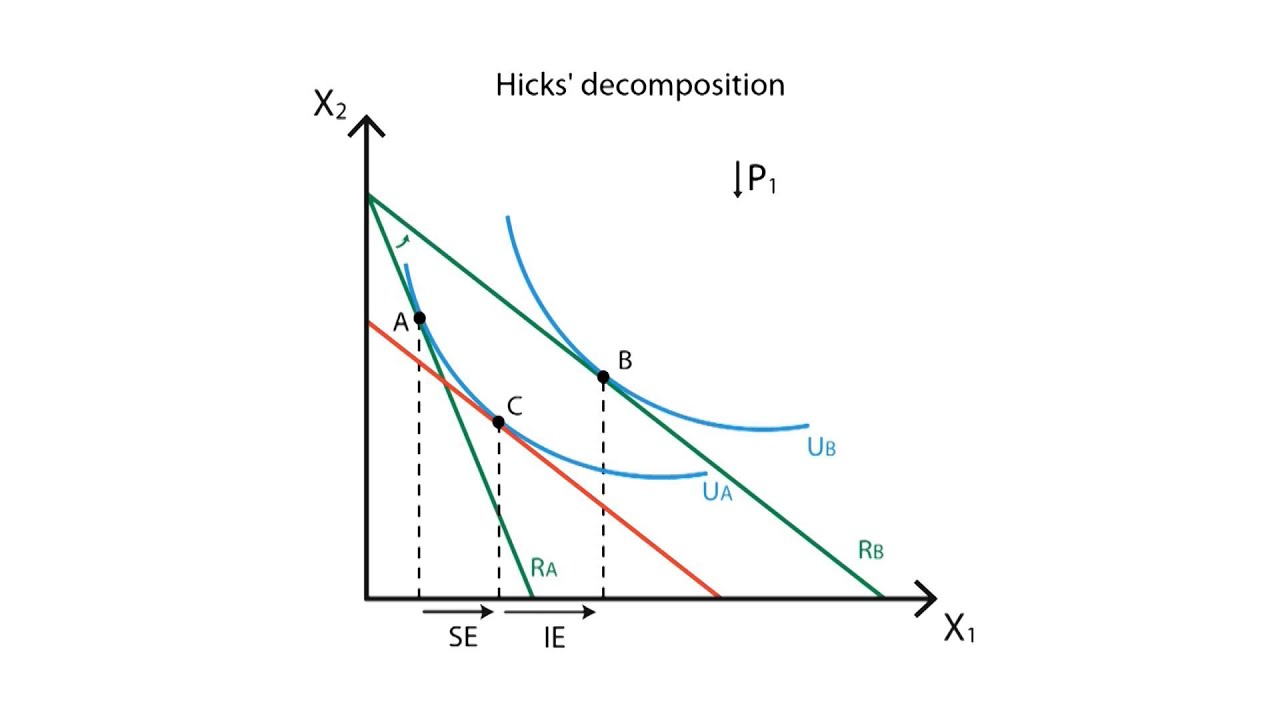
Income effect and substitution effect are the components of price effect i e. So his labour supply curve bends back to the left. The income effect of a rise in the hourly wage rate. A works fewer hours as the wage rate rises.
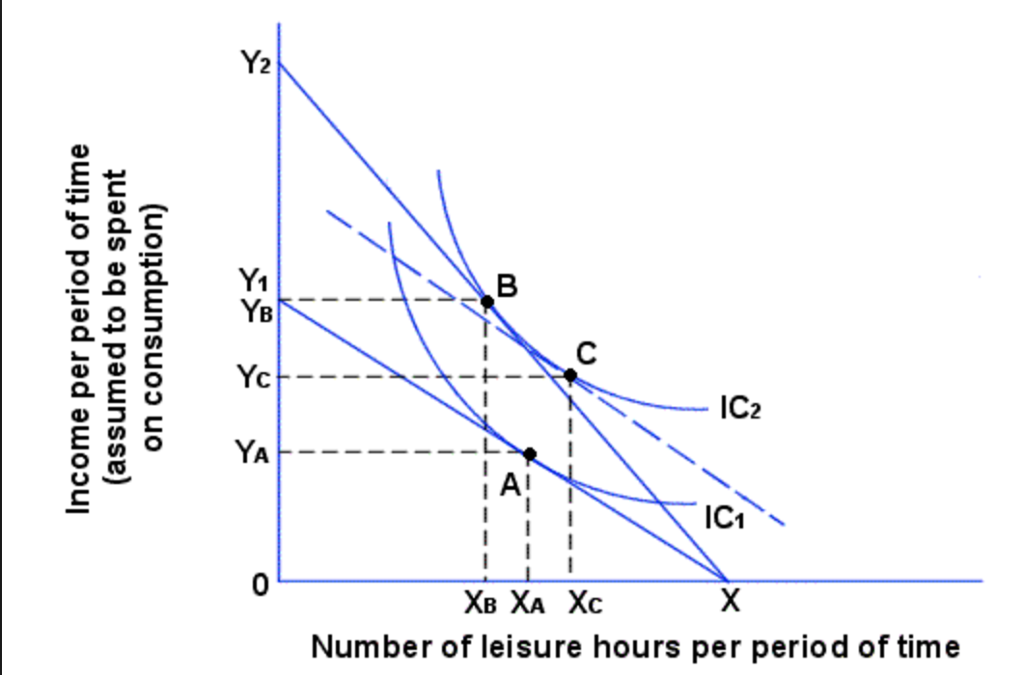
This is essential to a fundamental knowledge of labor market economics as we understand it today. When higher wages cause people to want to work more hours in order to reach a target desired income. Income effect refers to the change in the demand of a commodity caused by the change in consumer s real income. The decrease in quantity demanded due to increase in price of a product.
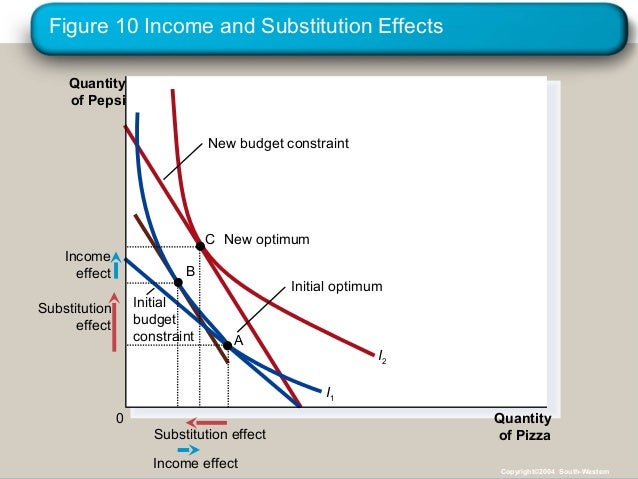
The income effect expresses the impact of increased purchasing power on consumption while the substitution effect describes how consumption is. 11 we see that bread being a normal good the fall in its price led the consumer to buy more of it as a result of consumer s real income gain. If leisure is an inferior good both substitution effect and income effect work in the same. When a target income has been reached and people prefer.
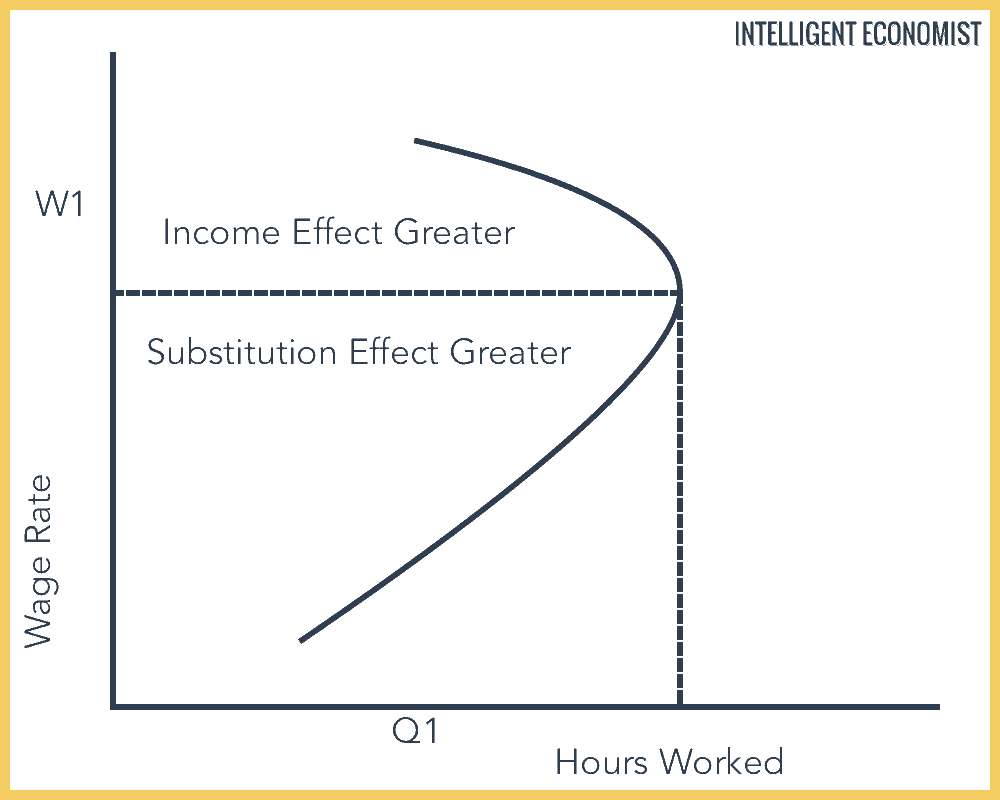
Income effect arises because a price change changes a consumer s real income and substitution effect occurs when consumers opt for the product s substitutes. Substitution effect means an effect due to the change in price of a good or service leading consumer to replace higher priced items with lower prices ones. P second the opportunity cost or price of leisure is the wage an individual can earn. Many studies have demonstrated that the price elasticity of labor supply is positive meaning that the substitution effect dominates more than the income effect in aggregate.
She substitutes some of her leisure time for additional hours of work. In case of normal goods both the income effect and substitution effect move in the same direction. One possibility is that over some range of labor hours supplied the substitution effect will dominate. Because the marginal.