Income Vs Wealth Effect

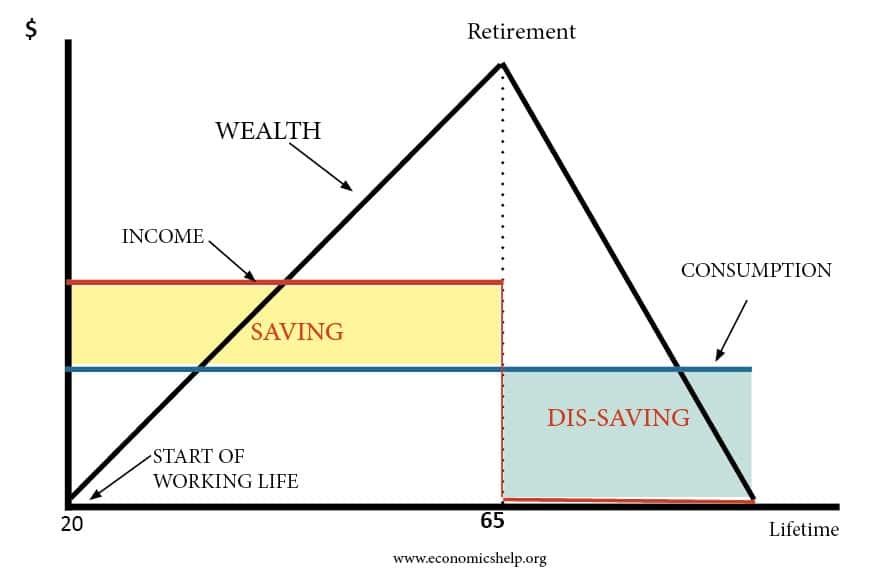
The wealth effect is a behavioral economic theory suggesting that consumers spend more when their wealth increases even if their income does not.
Income vs wealth effect. I like to think of income as the amount of money someone receives on a regular basis while wealth is the length of time that person or family could maintain their current lifestyle without receiving compensation for performing additional work. It is almost the same concept as the wealth effect that when the price of a good goes down your real income your purchase power increases so you increase consumption of that good. 27 2019 10 25 am et. These ratios are up from 3 4 and 28 in 1983 respectively.
On the other end wealth contains cash real estate individual properties such as ornaments and cars. Income makes capital or wealth while having wealth can assist an individual in adoring the outcome of his labor. On the other hand middle income families saw their median net worth shrink by 20 and lower income families experienced a loss of 45. Income is a flow of money going to factors of production.
Wealth effect income effect substitution effect. Income is not the same as wealth. As of 2016 upper income families had 7 4 times as much wealth as middle income families and 75 times as much wealth as lower income families. Income contains a definite amount of money.
Wealth includes income but also the total value of a. 1 wages and salaries paid to people from their jobs. Income decides your standard of living but wealth gives you control over the shape and future course of the economy. 3 profits flowing to businesses and dividends distributed to shareholders.
The wealth effect is the change in spending that accompanies a change in perceived wealth. 2 money paid to people receiving welfare benefits such as the state pension and tax credits. Income is generally understood to cover a person s earnings from their employment dividends from shares and stocks pension payments etc.