Income And Substitution Effect Example Problems

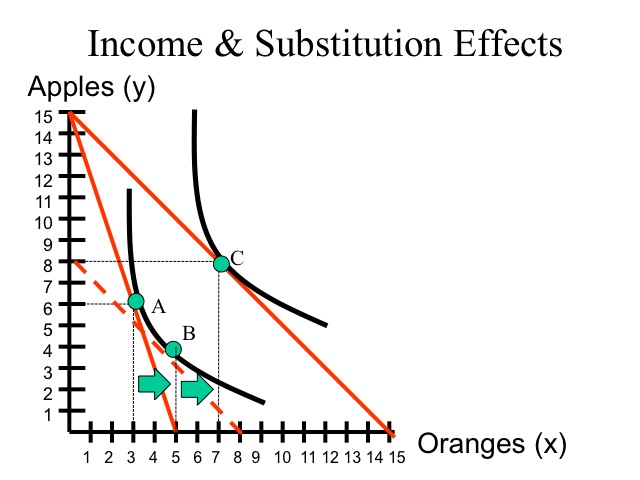
The substitution effect also led to an increase in consumption of bread.
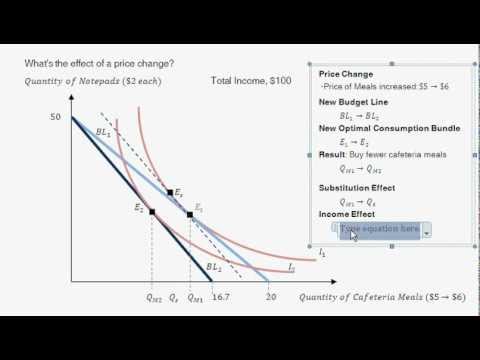
Income and substitution effect example problems. As a result consumers switch away from the good toward its substitutes. Practical example of substitution effect. Income and substitution effect for interest rates and saving. In case of normal goods both the income effect and substitution effect move in the same direction.
For example when the price of a good rises it becomes more expensive relative to other goods in the market. The total change in demand 4. The example discussed above is a normal good and hence the substitution effect and income effect work in tandem. The net effect equal the difference between substitution effect and income effect.
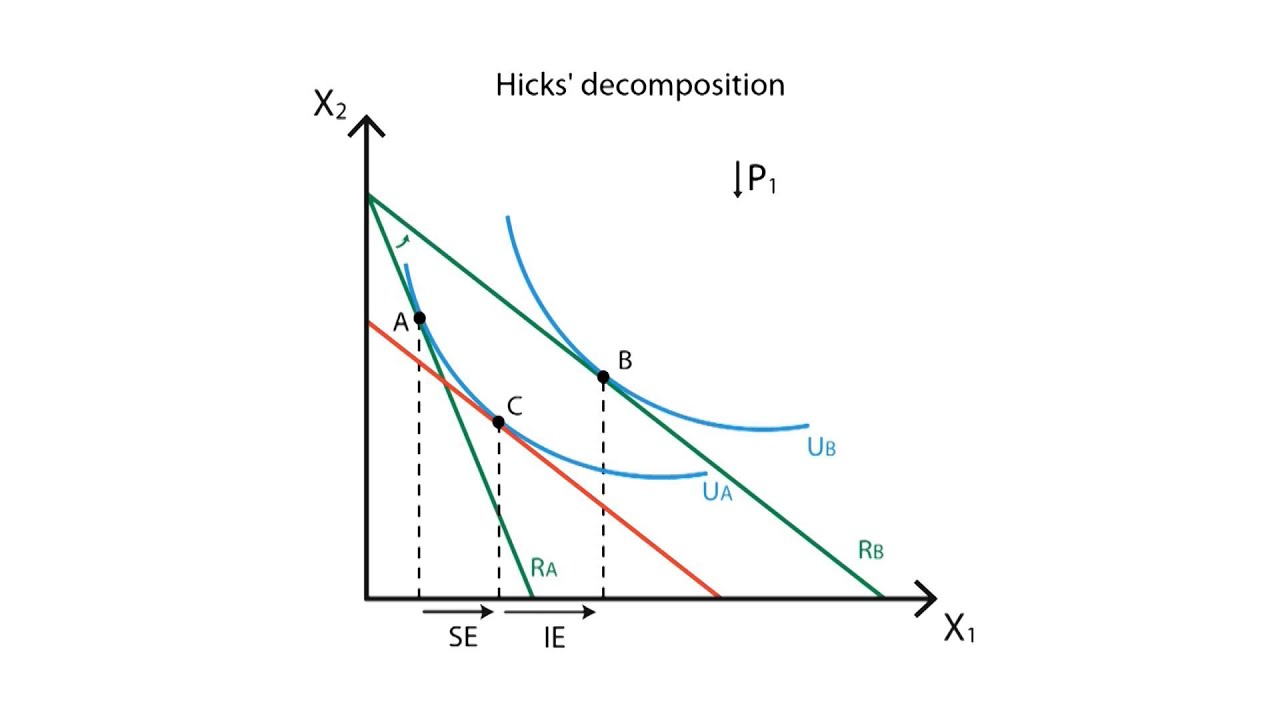
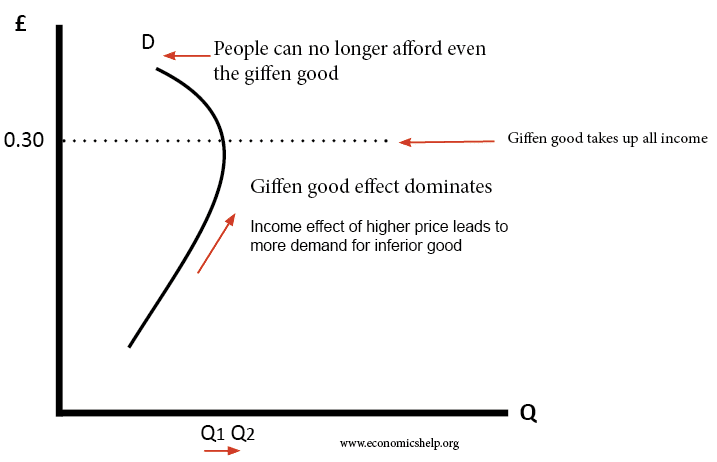
The substitution effect describes how consumption is impacted by changing relative income and prices. Higher interest rates increase income from saving. The substitution effect relates to the change in the quantity demanded resulting from a change in the price of good due to the substitution of relatively cheaper good for a dearer one while keeping the price of the other good and real income and tastes of the consumer as constant. In case of an inferior goods also called giffen good the income effect and substitution effect work in opposite directions i e.
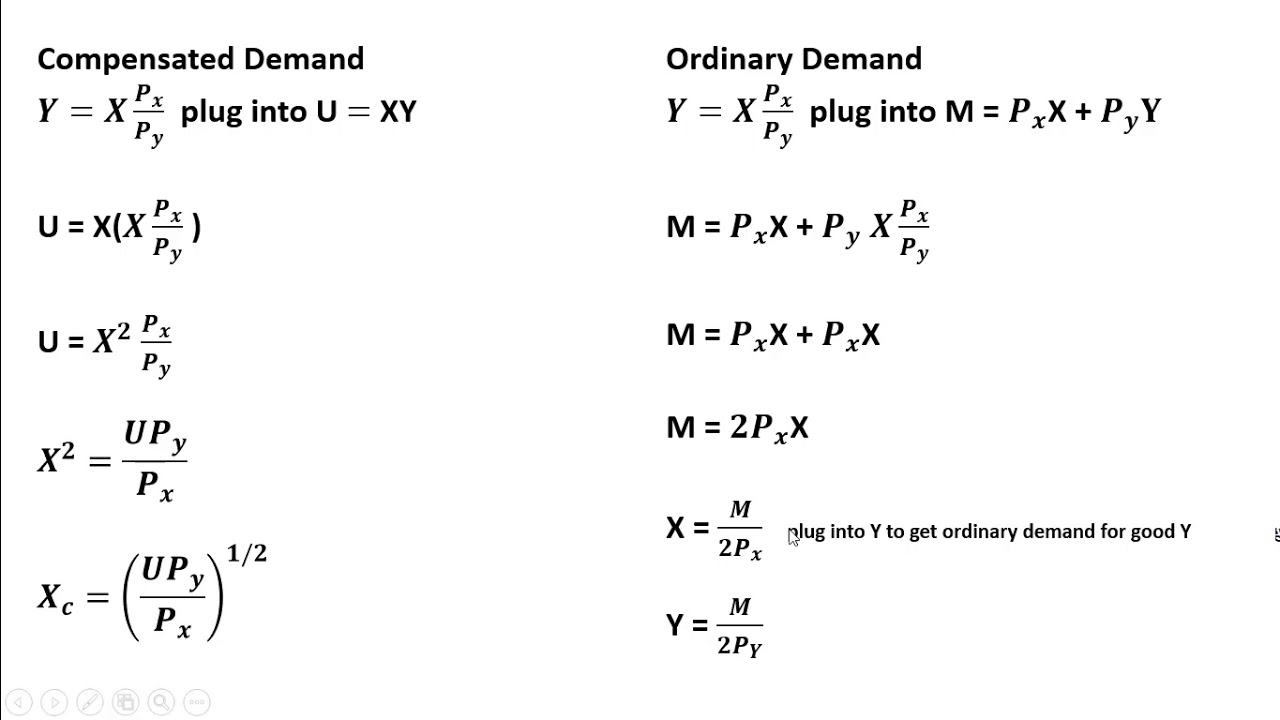
The substitution effect dominates the income effect then the net result of a decrease in the price of x will be an increase in the quantity of x consumed even if the income effect reduces the quantity of x consumed. Consider the following example. Income and substitution effects a summary what are income and substitution effects. Many studies have demonstrated that the price elasticity of labor supply is positive meaning that the substitution effect dominates more than the income effect in aggregate.
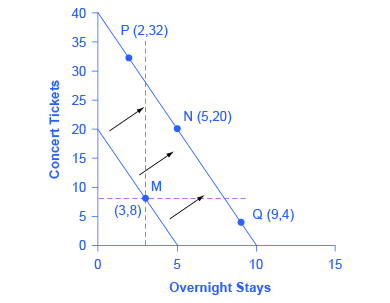
Example calculating income and substitution effects. If you have a lot of debts and spending commitments the income effect will take a long time to occur. 11 we see that bread being a normal good the fall in its price led the consumer to buy more of it as a result of consumer s real income gain. There is a bizarre but theoretically possible case where the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
Aggregated income and substitution effects. John eats rice that costs 5 per pound and pasta that costs 10 per pound. Therefore this gives consumers more income to spend and spending may rise income effect. The income effect expresses the impact of higher purchasing power on consumption.
The income effect will soon dominate. When the price of q1 p1 changes there are two effects on the consumer first the price of q1 relative to the other products q2 q3.